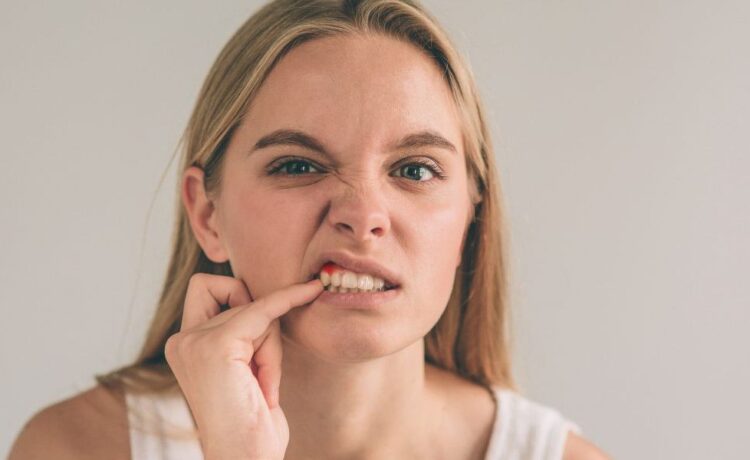
Gingivitis, a common form of gum disease, is a condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Though often mild in its initial stages, if left untreated, it can lead to severe dental complications. People often overlook the symptoms of gingivitis, mistakenly assuming they’re normal. The most common signs include red, swollen gums that bleed easily, particularly after brushing or flossing. There may also be persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
Causes of Gingivitis
The primary cause of gingivitis or tartar the accumulation of plaque, a bacteria-laden film that builds up on the teeth over time. Lifestyle factors can also contribute to its development, including smoking, poor oral hygiene, age, and certain medications.
The Impact of Gingivitis on Oral Health
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can develop into periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. This can eventually lead to tooth loss due to destruction of the tissue and bone that support your teeth.
Prevention and Treatment
Gingivitis can generally be prevented and treated through regular, thorough oral hygiene. This includes twice-daily tooth brushing, daily flossing, and regular dental check-ups. If you’re already experiencing symptoms of gingivitis, your dentist may recommend a professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from your teeth.
Gingivitis and Overall Health
It’s important to understand that gingivitis isn’t just a dental concern; it can affect your overall health. Research has suggested a link between gum disease like gingivitis and other health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. Inflammation in your gums could be linked to inflammation in other parts of your body, hence, maintaining good oral health is crucial not just for your mouth, but for the rest of your body as well.
At-Home Remedies for Gingivitis
While professional help is crucial, there are several at-home remedies that can help manage gingivitis. Rinsing with a warm saltwater solution can help soothe swollen, inflamed gums. Over-the-counter mouthwashes with antimicrobial properties can also aid in reducing plaque and preventing gum disease. However, these should be used as complements to, not replacements for, regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups.
The Role of Diet in Preventing Gingivitis
Your diet also plays a significant role in preventing gingivitis. Consuming a well-balanced diet that is high in vitamin C and calcium can strengthen your gums and teeth, making them less susceptible to gingivitis. Foods rich in antioxidants, particularly those found in cranberries, blueberries, and other fruits, can help your body repair damaged tissues, including your gums.
Coping with Gingivitis: The Emotional Aspect
Aside from the physical health implications, gingivitis can also affect an individual emotionally. The discomfort and embarrassment caused by symptoms like bad breath and bleeding gums can lead to anxiety and self-consciousness, impacting one’s social interactions and overall quality of life. It’s essential to remember that gingivitis is a common condition, and seeking professional help is the first step towards recovery.
Gingivitis in Children: A Special Concern
Children are not immune to gingivitis. In fact, the occurrence of gingivitis can be quite high in children and adolescents. Poor oral hygiene habits, hormonal changes during puberty, improper nutrition, and certain medications can make children prone to gingivitis. Parents and caregivers need to ensure that children maintain good oral hygiene habits from a young age, including regular brushing and flossing, and that they receive regular dental check-ups. If a child shows any signs of gingivitis, such as red or swollen gums, it’s crucial to get a dental consultation as soon as possible.
Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis: Understanding the Difference
While both gingivitis and periodontitis are forms of gum disease, it’s important to understand the differences between them. Gingivitis is the milder, initial stage of gum disease, and its symptoms can typically be reversed with proper oral care. On the other hand, periodontitis is a more advanced form of gum disease that results from untreated gingivitis. It involves inflammation and infection that spread beyond the gums to the ligaments and bone that support the teeth, which can ultimately lead to tooth loss.
The Role of Dental Professionals in Managing Gingivitis
While maintaining good oral hygiene at home is vital, the role of dental professionals cannot be overstated in managing gingivitis. They are equipped to provide comprehensive dental cleanings, remove hardened plaque (tartar), and reach areas that may be difficult for you to clean at home. Moreover, they can provide personalized advice based on your specific oral health needs. For example, if you have a tendency toward gum disease, they may recommend more frequent cleanings.
Conclusion
Gingivitis may be a common ailment, but it’s not one to be taken lightly. By recognizing the symptoms early and maintaining a strong oral hygiene routine, you can help protect your teeth and gums from this and other forms of gum disease. Regular dental checkups are also essential in maintaining oral health and preventing diseases like gingivitis.